Project management is the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet the project requirements. It involves planning, organizing, and managing resources to achieve specific goals and objectives within a defined timeline and budget. Effective project management ensures that a project is completed on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards.
Project management is a valuable skill for anyone who wants to be able to organize their work and achieve their goals. It is used in a wide range of industries, from construction and engineering to software development and marketing.
Understanding the 5 Key Phases of Project Management
Project management phases are structured steps that guide a project from start to finish. These phases ensure that all aspects of the project are carefully planned, executed, monitored, and completed. The most widely recognized framework for project management phases is defined by the Project Management Institute (PMI) in the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK). The five key phases are:

Initiation Phase
This phase is where the project is formally approved. The project manager defines the project goals, scope, and initial high-level plan. This includes getting buy-in from stakeholders and securing resources.
Objective: Define the project at a high level and obtain authorization.
Key Activities:
• Develop a project charter that outlines the project's purpose, objectives, scope, stakeholders, and key milestones.
• Identify key stakeholders and their roles.
• Conduct a feasibility study to assess the project's viability.
• Secure project approval and funding.
Planning Phase
In this phase, the project manager creates a detailed plan for how the project will be executed. This includes creating a work breakdown structure, identifying tasks and dependencies, estimating timelines and budgets, and assigning resources.
Objective: Establish a detailed roadmap to guide the project's execution and control.
Key Activities:
• Define the project scope and objectives in detail.
• Develop a work breakdown structure (WBS) to break down tasks.
• Create a project schedule with timelines and milestones.
• Identify resource requirements and assign roles.
• Develop a budget and allocate resources.
• Plan for risk management by identifying potential risks and creating mitigation strategies.
• Develop a communication plan to ensure stakeholders are informed.
Execution
This is where the actual work of the project is carried out. The project manager leads the team in completing the tasks outlined in the plan. This phase involves ongoing communication, monitoring progress, and managing risks.
Objective: Complete the work defined in the project management plan to meet the project’s objectives.
Key Activities:
• Coordinate and manage project resources.
• Execute tasks as per the project plan.
• Implement the project management plan, including quality assurance and risk management plans.
• Communicate with stakeholders and keep them updated on project progress.
• Monitor project performance and make adjustments as necessary.
Monitoring and Controlling
Throughout the execution phase, the project manager closely monitors progress against the plan. This involves identifying any deviations from the plan and taking corrective action as needed.
Objective: Track, review, and regulate the project and performance; identify any areas where changes are required.
Key Activities:
• Measure project performance using key performance indicators (KPIs).
• Track progress against the project plan, schedule, and budget.
• Identify any variances and implement corrective actions.
• Manage changes to the project scope, schedule, and costs through change control processes.
• Ensure that project deliverables meet the required quality standards.
Closing
This phase signifies the formal completion of the project. The project manager finalizes all outstanding work, delivers the project deliverables, and documents lessons learned. The project team is disbanded, and resources are released.
Objective: Finalize all project activities, deliver the project, and formally close the project.
Key Activities:
• Ensure all project deliverables are completed and meet the project requirements.
• Obtain formal acceptance of the project deliverables from stakeholders.
• Conduct a project closure meeting and hand over project documentation.
• Release project resources and provide final reports.
• Document lessons learned and archive project documents for future reference.
These phases provide a structured approach to managing projects, ensuring that all aspects are carefully planned, executed, monitored, and completed. Effective project management requires attention to detail in each phase to achieve the desired outcomes and deliver value to stakeholders.
What is a Project Cycle?
A project cycle refers to the sequence of phases that a project goes through from its initiation to its completion. This cycle ensures that a project is systematically planned, executed, monitored, and closed. The concept of a project cycle provides a structured approach to project management, helping to ensure that projects meet their objectives and deliver expected outcomes.
Project Cycle vs. Project Management
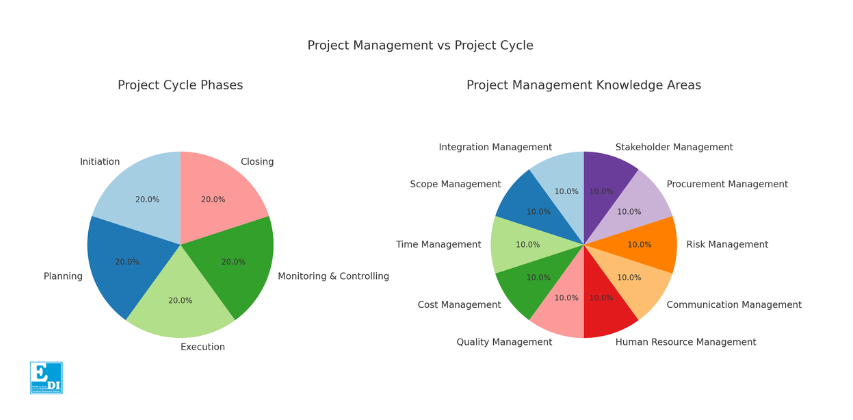
Project cycle and project management are related concepts, but they focus on different aspects of handling projects. Here's a detailed comparison to highlight their distinctions and relationships:
1. Scope:
• Project Cycle: Refers to the phases a project goes through from start to finish.
• Project Management: Involves the methodologies, processes, and tools used to manage and execute a project.
2. Focus:
• Project Cycle: Focuses on the sequence of stages and their specific objectives.
• Project Management: Focuses on the application of skills and techniques to manage the project effectively.
3. Process vs. Practice:
• Project Cycle: More about the overall process and life-cycle of a project.
• Project Management: More about the practices, strategies, and tools used within each phase of the project cycle.
4. Implementation:
• Project Cycle: Provides a framework for what needs to be done at each stage.
• Project Management: Provides the approach and methods to execute tasks within the framework.
In summary, the project cycle outlines the stages a project goes through, while project management involves the methodologies and practices used to manage and execute the project through these stages effectively. Both concepts are intertwined, as effective project management is essential to navigate successfully through the project cycle.
Core Knowledge Areas in Project Management
• Integration Management: Ensures that project processes are properly coordinated.
• Scope Management: Involves defining and controlling what is and is not included in the project.
• Time Management: Concerned with the timely completion of the project.
• Cost Management: Planning, estimating, budgeting, and controlling costs.
• Quality Management: Ensuring that the project meets the required quality standards.
• Human Resource Management: Organizing, managing, and leading the project team.
• Communication Management: Ensuring timely and appropriate generation, collection, distribution, and storage of project information.
• Risk Management: Identifying, analyzing, and responding to project risks.
• Procurement Management: Acquiring goods and services from external sources.
• Stakeholder Management: Identifying and managing project stakeholders and their expectations.
Key Benefits of Project Management
• Improved Efficiency: Streamlined processes and clear guidelines.
• Enhanced Communication: Clear channels for stakeholder communication.
• Better Risk Management: Proactive identification and mitigation of risks.
• Cost Control: Effective budgeting and cost management.
• Quality Assurance: Adherence to quality standards and customer satisfaction.
• Goal Alignment: Ensuring project outcomes align with organizational objectives.
Effective project management is critical for the success of any project, helping to ensure that it is completed on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards.
At EDI, we help project managers, coordinators and professionals from all disciplines to plan, identify, design projects to achieve successful results with good impact through our professional development course on Project Management. Our course will help you gain a foundational understanding of the different stages of a project life cycle, from initiation to closing, and teach you practical skills like planning, scheduling, budgeting, and resource management.
Join our comprehensive Project Management course today & master the art of successful project delivery.
For more information please write to us at business@edi-cambodia.org or call us at 092 888 955 | 015 728 123.
Develop Your People, Grow Your Business


.png)

.png?alt=media&token=b9d6ff4b-eeab-415a-a609-054cc43e8062)


 Primary School Knowledge & Methodology.jpg)